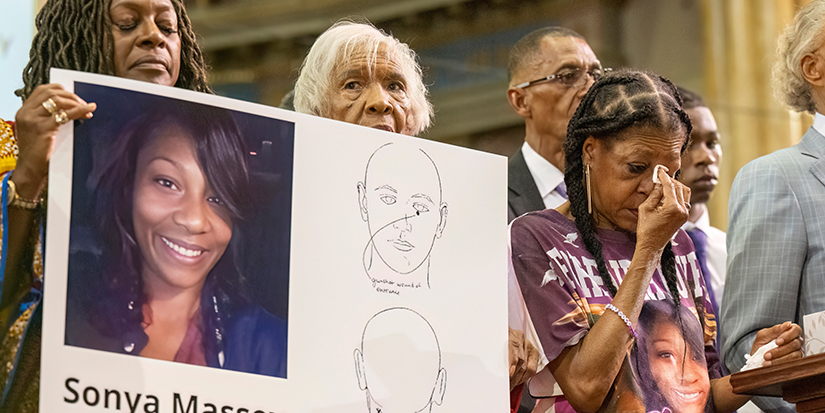International
Illinois deputy found guilty of murder in the shooting of Sonya Massey, a Black woman who called 911
Published 12:39 PDT, Wed October 29, 2025
—
PEORIA, Ill. (AP) — An Illinois jury on Wednesday convicted a former sheriff’s deputy of second-degree murder in the shooting death of Sonya Massey, a Black woman who called 911 asking for help.
Sean Grayson, 31, could be sentenced to up to 20 years in prison, or probation.
Grayson and another deputy arrived at Massey’s home in Springfield, Illinois, early on the morning of July 6, 2024, after she reported a prowler. Grayson shot the 36-year-old woman after confronting her about how she was handling a pot of hot water she had removed from her stove. Grayson and his attorneys argued that he feared Massey would scald him with the hot water.
Massey’s killing raised new questions about U.S. law enforcement shootings of Black people in their homes, and prompted a change in Illinois law requiring fuller transparency on the background of candidates for law enforcement jobs.
Grayson originally was charged with first-degree murder, which carries a prison sentence of 45 years to life, which must be served in full. But after the seven-day trial, the jury was given the option of considering second-degree murder, which applies when a defendant faces a “serious provocation” or believes their action is justified even if that belief is unreasonable.
Second-degree murder could bring Grayson a sentence of four to 20 years with day-for-day good time, meaning his sentence could be halved if he behaves behind bars. He could also be sentenced to probation and avoid prison time entirely.
Body camera video recorded by the other Sangamon County Sheriff’s deputy on the scene that morning, Dawson Farley, was a key part of the prosecution’s case. It showed Massey, who struggled with mental health issues, telling the officers, “Don’t hurt me,” and repeating, “Please God.”
When the deputies entered the house, Grayson saw the pot on the stove and ordered Massey to move it. Massey jumped up to retrieve the pot and she and Grayson joked about how he said he was backing off from the “hot, steaming water.” Massey then replied, “I rebuke you in the name of Jesus.”
Both Grayson and Farley drew their pistols and yelled at Massey to put the pot down. Grayson told investigators he thought her “rebuke” meant she intended to kill him and, in the following commotion, fired three shots, striking Massey just below the eye.
Farley, who at the time of the shooting was a probationary employee subject to firing for any reason, testified that Massey didn’t say or do anything that caused him to view her as a threat. But under cross-examination, he acknowledged that he initially reported to investigators that he feared for his safety because of the hot water. Farley did not fire his weapon and was not charged.
Grayson testified in his own defense and was the first witness his attorneys called. He told jurors he noticed the bottom of the pot was red and he believed Massey planned to throw the water at him. He said Massey’s words felt like a threat and that he drew his gun because officers are trained to use force to get compliance.
“She done. You can go get it, but that’s a head shot,” Grayson told Farley after the shooting. “There’s nothing you can do, man.”
Grayson relented moments later and went to get his kit while Farley found dish towels to apply pressure to the head wound. When Grayson returned, Farley told him his help wasn’t necessary, so he threw his kit on the floor and said, “I’m not even gonna waste my med stuff then.”
Prosecutors said that response indicated Grayson’s disregard for public safety, an argument that persuaded Judge Ryan Cadagin to keep Grayson in jail awaiting trial. An Illinois appellate court subsequently ruled that Grayson should be released under the Pre-Trial Fairness Act. An appeal to the state Supreme Court has yet to be decided.
Massey’s death also forced the early retirement of the sheriff who hired Grayson and generated a U.S. Justice Department inquiry. The federal probe was resolved with Sangamon County Sheriff’s Department’s agreement to fortify training, particularly de-escalation practices; develop a program in which mental health professionals can respond to emergency calls; and to generate data on use-of-force incidents.
Massey’s family, with the assistance of civil rights attorney Ben Crump, settled a lawsuit against the county for $10 million and state lawmakers changed Illinois law to require fuller transparency on the background of candidates for law enforcement jobs.
– John O'Connor, The Associated Press